Sustainability is increasingly moving to the top of many company agendas. As a result, investors increasingly require reporting on their ESG (Environment, Social and Governance) agenda with concrete actions to follow. What is the board’s role in guiding companies on this new path? What are the better practices that are emerging?
By Karen Loon IDP-C and IDN Board Member
In an increasingly fractured world, many of the significant global risks which the world faces relate to sustainability risks. These risks include climate action failure, human environmental damage, biodiversity loss and extreme weather. These risks, in addition to other challenges arising from the increasing adoption of technology, the pandemic and geopolitical risks are having a significant impact on companies and their boards.
What is the role of company boards to guide their companies on this new path? Further, what are some of the better practices which are emerging?
In a session facilitated by Liselotte Engstam IDP-C and IDN Board Member, INSEAD Directors Network (IDN) members, together with members of the INSEAD alumni Community Impact Challenge recently learnt more about these areas from Mats Magnusson, Professor in Product Innovation Engineering of the KTH Royal Institute of Technology, and Ludo Van der Heyden, Emeritus Professor of Technology and Operations Management, and the INSEAD Chaired Professor of Corporate Governance at INSEAD.
Increasing pressures require boards to better guide companies to renewal
Companies need to renew themselves more and faster than ever before.
“This renewal [is not] actually about becoming slightly better at things – it’s about changing things quite radically,” noted Mats Magnusson.
These changes are not only due to digital – organisations also need to address new values, with sustainability being one of them.
Mats added that various studies by academics and consultants have shown that companies have reacted differently to these challenges, with some trying to innovate, and others struggling because of the present pandemic. However, what is common to most of them is that companies realise that if they just continue the way they have been doing things the last few years, they will not be successful in the future. As a result, there is a huge need for innovation.
“Actually, a large part of that innovation has to address sustainability”, he added, something which is not new to boards.
Sustainability and climate change require all companies to revisit their purpose, strategy and business model.
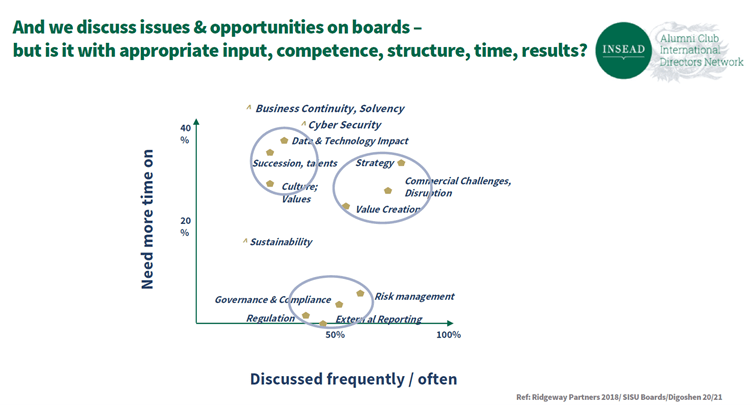
Based on research, most board members and directors agree that they spend a lot of time discussing governance about risk, regulation, and reporting, which is necessary.
However, there are several aspects that boards are not discussing enough. These includes sustainability, as well as culture and new technologies. Finally, boards need to spend more time on their strategy, value creation disruption, innovation.
These are not new findings; however, boards do need to improve their level of discussion on these areas to ensure that they are addressing them.
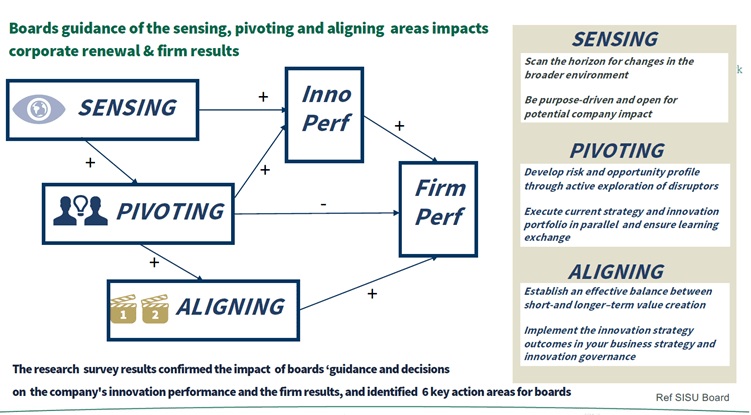
The importance of sensing, pivoting and aligning by boards
Three dynamic capabilities that boards can adopt are sensing, pivoting and aligning. Both sensing and pivoting have a positive correlation with innovation performance. Further, aligning positively impacts firm performance. However, pivoting can also harm firm performance.
Areas which boards can work on:
- Sensing – Look at the external world and understand what is changing and impacting us, whether technology, business, customers or the environment. Become better at scanning the horizon for changes with an open mind. Observe changes in the broader environment, not only in your own industry but adjacent and completely different industries. For example, technology-wise, this may mean that companies need to consider completely new technologies that they have not considered before. However, Mats notes that “what we should not address is to focus on our purpose. If we focus on our purpose, then we’ll have some kind of limitation once we are actually looking.”
- Pivoting – is about taking the right opportunities, taking action and daring to make strategic changes that include some form of innovation. Develop your company’s risk and opportunity profile by looking into the things disrupting your companies – perhaps new technologies, the new business models, or new companies. This information should be used to inform the company’s strategy.
- Aligning – This is about combining the new and the existing capabilities and business models. Find a good balance between the short-term value pressure – companies do need cash as well as longer-term value creation. It is essential to ensure that the innovation strategy is a key part of the business strategy.
Boards need to discuss their approach and capability to guide their company’s ESG agenda
Mats shared that more can be done by companies to integrate sustainability into their strategies. Of companies recently surveyed by SISU Boards:
- Lack of integration of sustainability into strategy – Almost 45% actually do not yet integrate sustainability into their strategy. Companies need to become more granular – set goals for the sustainability action and find ways of evaluating if the things they are doing are the right ones.
- Lack of board accountability for sustainability – As many as 60% of boards have not yet discussed how to engage and consider sustainability. For instance, should they have a committee focusing on this or several committees, and in what areas?
Boards can improve their sensing, pivoting and aligning capabilities
Boards can do more work to improve their capabilities when it comes to sustainability.
- Sensing – 46% don’t have good processes to foresee changes and impacts on sustainability and business. Additionally, 48% don’t actively monitor new solutions that expedite their business sustainability towards their purpose.
- Pivoting – 49% aren’t good at taking balanced risks towards ensuring corporate renewal. Further, 56% do not ensure that their strategy harnesses and reshapes the ecosystem for better sustainability and differentiation.
- Aligning – 51% are not yet good at balancing short- and long-term value creation. In addition, 61% have not yet implemented a clear and effective innovation system, monitoring innovation activities and culture.
Board best practices to experiment with
Ludo Van der Heyden suggested some case studies and best practices for board renewal on sustainability around sensing, pivoting and aligning.
He also noted that it is important to select a modern, ambitious and humble chair, and board members. Boards should also rethink their role and focus, using Fair Process Leadership as support.
It is critical to structure the board and the organisation for sensing, developing the capability of timely pivoting, and continuously aligning and re-aligning.
Finally, it is vital to have collective leadership at the board level, and that it is proactive and engaged.
INSEAD Directors Network (“IDN”) – An INSEAD Global Club of International Board Directors
Our Mission is to foster excellent Corporate Governance through networking, communication and self-improvement. IDN has 1,500 members from 80 countries, all Alumni from different INSEAD graduations as MBA, EMBA, GEMBA, and IDP-C. We meet in live IDN webinars and meet-ups arranged by our IDN Ambassadors based in 25 countries. Our IDN website holds valuable corporate governance knowledge in our IDN blog, and we share insights with our LinkedIn and Twitter followers. We highlight our member through quarterly sharing of their new board appointments, and once a year, we give out IDN Awards to prominent board accomplishments. We provide a peer-to-peer mentoring and board vacancy service, and we come together two times per year at the INSEAD Directors Forum arranged by ICGC. We also engage with ICGC on joint research.
INSEAD Corporate Governance Centre (“ICGC”)
Established in 2010, the INSEAD Corporate Governance Centre (ICGC) has been actively engaged in making a distinctive contribution to the knowledge and practice of corporate governance. The ICGC harnesses faculty expertise across multiple disciplines to teach and research on the challenges of boards of directors in an international context and to foster a global dialogue on governance issues with the ultimate goal to develop boards for high-performance governance. Visit ICGC website: https://www.insead.edu/centres/corporate-governance


